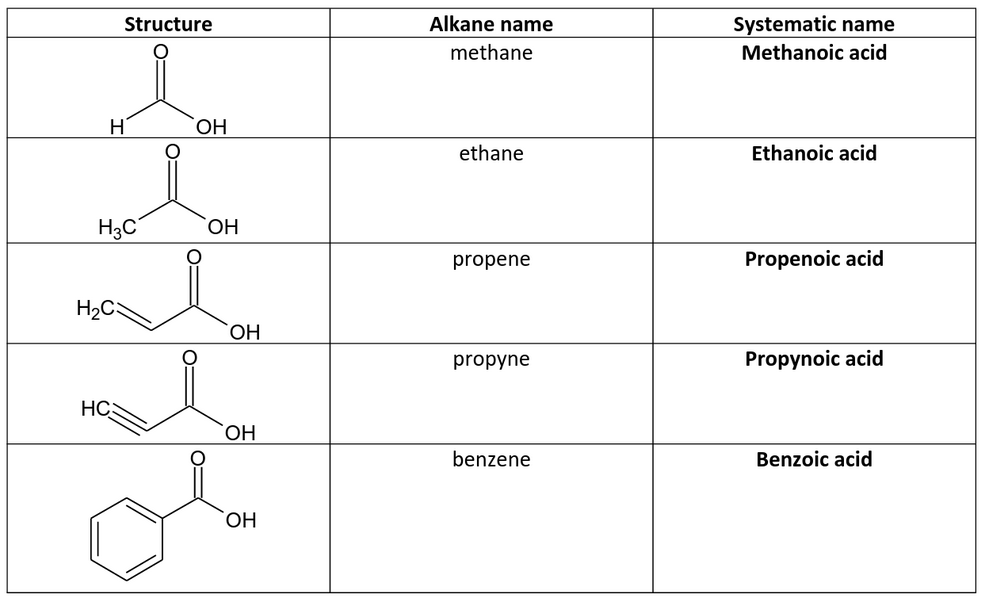
Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups . we saw in section 20.3 and section 24.5 that a carboxyl group is deprotonated and exists as the carboxylate anion at a physiological ph of 7.3, while an. amino acid, any of a group of organic molecules that consist of a basic amino group (―nh 2), an acidic carboxyl group (―cooh), and an organic. each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded. amino acids are linked to each other by peptide bonds, in which the carboxyl group of one amino acid is joined to the amino. each amino acid contains a central c atom, an amino group (nh2), a carboxyl group (cooh), and a specific r group. amino acids have a central asymmetric carbon to which an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a side chain (r group) are attached.
from www.lecturio.com
each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded. we saw in section 20.3 and section 24.5 that a carboxyl group is deprotonated and exists as the carboxylate anion at a physiological ph of 7.3, while an. amino acids are linked to each other by peptide bonds, in which the carboxyl group of one amino acid is joined to the amino. amino acids have a central asymmetric carbon to which an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a side chain (r group) are attached. each amino acid contains a central c atom, an amino group (nh2), a carboxyl group (cooh), and a specific r group. amino acid, any of a group of organic molecules that consist of a basic amino group (―nh 2), an acidic carboxyl group (―cooh), and an organic.
Carboxylic Acids and their Derivatives Medical Library
Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups amino acids have a central asymmetric carbon to which an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a side chain (r group) are attached. amino acids have a central asymmetric carbon to which an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a side chain (r group) are attached. each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded. amino acids are linked to each other by peptide bonds, in which the carboxyl group of one amino acid is joined to the amino. amino acid, any of a group of organic molecules that consist of a basic amino group (―nh 2), an acidic carboxyl group (―cooh), and an organic. we saw in section 20.3 and section 24.5 that a carboxyl group is deprotonated and exists as the carboxylate anion at a physiological ph of 7.3, while an. each amino acid contains a central c atom, an amino group (nh2), a carboxyl group (cooh), and a specific r group.
From bio1151.nicerweb.com
carboxyl.html 04_10cChemicalGroupsL.jpg Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups amino acids have a central asymmetric carbon to which an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a side chain (r group) are attached. each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded. each amino acid contains a central c atom,. Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups.
From www.coursehero.com
[Solved] Draw an amino acid and label the following amino group Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups amino acids have a central asymmetric carbon to which an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a side chain (r group) are attached. each amino acid contains a central c atom, an amino group (nh2), a carboxyl group (cooh), and a specific r group. amino acid, any of a group of organic molecules that. Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups.
From sphweb.bumc.bu.edu
Nucleic Acids Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups each amino acid contains a central c atom, an amino group (nh2), a carboxyl group (cooh), and a specific r group. amino acids are linked to each other by peptide bonds, in which the carboxyl group of one amino acid is joined to the amino. each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a. Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups.
From education-portal.com
Carboxylic Acid Structural Formula, Properties & Uses Video & Lesson Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups amino acids are linked to each other by peptide bonds, in which the carboxyl group of one amino acid is joined to the amino. amino acid, any of a group of organic molecules that consist of a basic amino group (―nh 2), an acidic carboxyl group (―cooh), and an organic. we saw in section 20.3 and section. Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups.
From www.dreamstime.com
Amino Acid Labeled Diagram Vector Illustration Drawing Biochemistry Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups amino acids have a central asymmetric carbon to which an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a side chain (r group) are attached. each amino acid contains a central c atom, an amino group (nh2), a carboxyl group (cooh), and a specific r group. each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists. Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups.
From microbenotes.com
Amino Acids Properties, Structure, Classification, Functions Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded. we saw in section 20.3 and section 24.5 that a carboxyl group is deprotonated and exists as the carboxylate anion at a physiological ph of 7.3, while an. amino acids have a central asymmetric. Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups.
From saylordotorg.github.io
Carboxylic Acids Structures and Names Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups amino acids have a central asymmetric carbon to which an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a side chain (r group) are attached. each amino acid contains a central c atom, an amino group (nh2), a carboxyl group (cooh), and a specific r group. amino acid, any of a group of organic molecules that. Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups.
From www.thesciencehive.co.uk
Biological Molecules (A Level) — the science hive Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups amino acids have a central asymmetric carbon to which an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a side chain (r group) are attached. each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded. amino acid, any of a group of organic. Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups.
From www.lecturio.com
Basics of Amino Acids Concise Medical Knowledge Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups amino acid, any of a group of organic molecules that consist of a basic amino group (―nh 2), an acidic carboxyl group (―cooh), and an organic. each amino acid contains a central c atom, an amino group (nh2), a carboxyl group (cooh), and a specific r group. amino acids have a central asymmetric carbon to which an. Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups.
From www.expii.com
Amino Acids — Overview & Structure Expii Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups amino acids have a central asymmetric carbon to which an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a side chain (r group) are attached. we saw in section 20.3 and section 24.5 that a carboxyl group is deprotonated and exists as the carboxylate anion at a physiological ph of 7.3, while an. each amino acid. Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups.
From faculty.samford.edu
Cell Chemistry Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups amino acids have a central asymmetric carbon to which an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a side chain (r group) are attached. we saw in section 20.3 and section 24.5 that a carboxyl group is deprotonated and exists as the carboxylate anion at a physiological ph of 7.3, while an. amino acids are. Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups.
From www.compoundchem.com
A Brief Guide to the Twenty Common Amino Acids Compound Interest Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups each amino acid contains a central c atom, an amino group (nh2), a carboxyl group (cooh), and a specific r group. each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded. we saw in section 20.3 and section 24.5 that a carboxyl group is. Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups.
From www.coursehero.com
Amino Acids Structure Nutrition Course Hero Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups amino acids have a central asymmetric carbon to which an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a side chain (r group) are attached. each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded. we saw in section 20.3 and section 24.5. Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups.
From www.lecturio.com
Basics of Amino Acids Concise Medical Knowledge Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups we saw in section 20.3 and section 24.5 that a carboxyl group is deprotonated and exists as the carboxylate anion at a physiological ph of 7.3, while an. amino acids have a central asymmetric carbon to which an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a side chain (r group) are attached. each amino acid. Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
Proteins OpenStax Biology 2e Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups we saw in section 20.3 and section 24.5 that a carboxyl group is deprotonated and exists as the carboxylate anion at a physiological ph of 7.3, while an. each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded. each amino acid contains a central. Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups.
From psychology.wikia.com
Carboxylic acid Psychology Wiki Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups we saw in section 20.3 and section 24.5 that a carboxyl group is deprotonated and exists as the carboxylate anion at a physiological ph of 7.3, while an. each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded. each amino acid contains a central. Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups.
From www.youtube.com
Carboxylic Acids and the Carboxyl Group YouTube Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups amino acids have a central asymmetric carbon to which an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a side chain (r group) are attached. we saw in section 20.3 and section 24.5 that a carboxyl group is deprotonated and exists as the carboxylate anion at a physiological ph of 7.3, while an. amino acids are. Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups.
From www.dreamstime.com
Carboxyl (carboxy) Group. Functional Group is Defined As Carbonyl and Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups each amino acid contains a central c atom, an amino group (nh2), a carboxyl group (cooh), and a specific r group. amino acids are linked to each other by peptide bonds, in which the carboxyl group of one amino acid is joined to the amino. amino acids have a central asymmetric carbon to which an amino group,. Do Amino Acids Have Carboxyl Groups.